|
 |
 |
 |


Appendix A
PEGGER Software ManualAbout this Manual Installing PEGGER Read the terms of the license agreement and select ‘I accept the agreement’ if you wish to install the software. Select Next to continue. Select a location for PEGGER to be installed. Most of the files that PEGGER installs will be in the ArcView installation directory so less than 1 MB of files will be placed in the installation directory chosen here. Accept the default location and select Next to continue. All installations will include the PEGGER ArcView extension and the integrated help files. If you do not wish to install the tutorial, select Minimal. The Compact installation includes the PEGGER tutorial with only the three shapefile datasets for those who do not have Spatial or 3D Analyst. The Full installation includes the PEGGER tutorial and all the tutorial datasets: three shapefiles, a GRID elevation model, and a TIN for those who have Spatial or 3D analyst and wish to use the Survey P-Line function with RoadEng. Select a folder to place the program shortcuts in the start menu. Either the default location or the ESRI\ArcView GIS 3.x folder work well. Review the installation settings and select Install to complete the installation. A completion screen will appear if you have installed PEGGER successfully. You should now have a new item under your start menu called PEGGER with shortcuts to the PEGGER Tutorial, the PEGGER Help file and the un-installation program depending on which installation components were selected. Uninstalling PEGGER
Finding Help All of the tools, dialogs and menus that are part of the PEGGER
extension have context based help that can be viewed in the status
bar at the bottom of the ArcView application window. In addition
using the View Help tool: Using Tutorial.apr The tutorial project file opens with the three shapefiles already symbolized and added to a view. If you have Spatial Analyst or 3D Analyst you can also add the DEM or TIN to the view. First, enable the Spatial Analyst or 3D Analyst Extension by selecting Extensions under the File menu and selecting 3D or Spatial Analyst.
Then, using the Add Theme Button: Activating the Extension
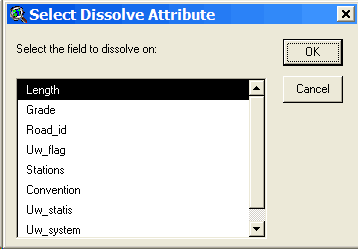
The road theme Grade attribute Open the attribute table for the road theme by making the road
theme the active theme (select it in the view legend), and selecting
Theme > Table or by using the Open Theme Table button: Look at the fields in the table to determine if there is an appropriate field for storing grade information. In this case, the Grade field looks like it will work, but it is always good to check to make sure it is a numeric field. Select the Grade field and look under the Field menu. If the statistics menu item is not grayed out, then it is a numeric field (it will be grayed out if it is a text field). If you want to add a new field to the table to store grade information, you will need to start editing the table, and then add a new field of type number. If you would like more information, lookup “editing a table” in the ArcView help file index Name attribute Open the attribute table for the road theme by making the road
theme the active theme and selecting Theme > Table or by using
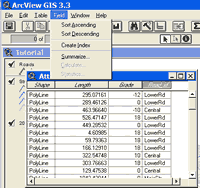
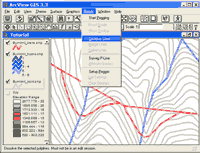
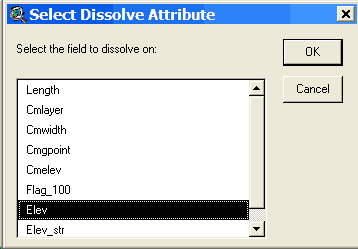
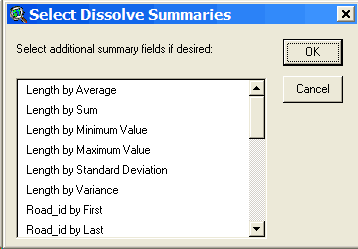
the Open Theme Table button: Look at the fields in the table to determine if there is an appropriate field for storing road name information. In this case, the Road_id field looks like it will work, but it is always good to check to make sure it is a text field. Select the Road_id field and look under the Field menu. If the statistics menu item is grayed out then it is a text field. If you want to add a new field to the table to store road name information, you will need to start editing the table, and then add a new field of type string. If you would like more information, lookup “editing a table” in the ArcView help file index. The contour theme Elevation attribute In order to use a contour theme with PEGGER, a numeric attribute in the contour theme must store the elevation values of the contours. Check to make sure that the contour theme has a numeric elevation value field by opening the table and looking at the themes attributes. If the contour theme attribute table does have an elevation field but the values are stored as strings rather than numbers, they will need to be converted before being used with PEGGER. For more information, lookup “elevation data” in the ArcView help file index. Contour Interval Subset data After selecting the contours in the area you will be pegging, select Theme > Convert to Shapefile and save the new dataset. This dataset will automatically be added to the active view and displayed. Create an index Select the elevation attribute field heading and then choose Field > Create Index to create the attribute index. If the there is a Remove Index instead of Create Index under the Field menu, then the elevation attribute is already indexed. Dissolve contours Make the contour theme the active theme and select Dissolve Lines under the Roads menu. When asked, select the elevation field in the contour dataset as the field to dissolve on.
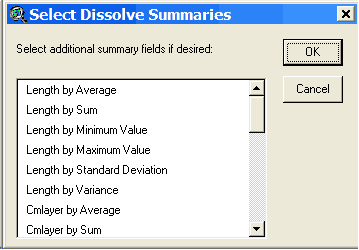
Optionally, you can select additional fields to summarize in the output attribute table. If you don’t want any additional fields to be summarized, select OK.
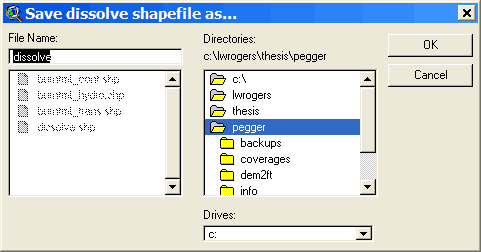
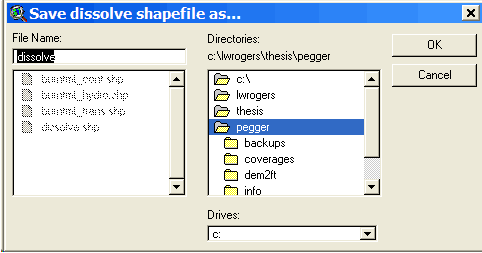
Choose a location to store the output shapefile.
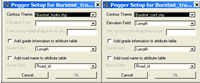
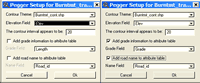
Additional Themes You may wish to add additional datasets to the view for use while you are pegging. Streams, slope class information, existing roads, unstable slopes are all common datasets that may be added into the view in order to better inform the pegging process. Setup Pegger To setup PEGGER, make the desired road theme the active theme and select Setup Pegger from the Roads menu. You can setup PEGGER both inside and outside of a pegging session. Selecting Setup Pegger will open the PEGGER Setup dialog where you can select a contour theme to use and whether or not to add grade and road name information to the attribute table while pegging. First, select the Contour Theme that you will use as the elevation model for your work area. Once you have selected a contour theme the Elevation Field will be populated with numeric attributes from the contour theme attribute table. For more information about the required attribute format, see Elevation Item in the Contour Theme section. Select the field in the attribute table that stores the elevation information for each contour. Once an elevation field is selected, PEGGER will attempt to determine the contour interval of the contour dataset. If PEGGER can not determine the contour interval then it can be manually entered in the Contour Interval box. Optionally, PEGGER can keep track of grade and road name information in the attribute table of the pegged road theme. The grade and road name information can be helpful in performing additional analyses in the GIS or for truck performance modeling, costing, etc. If desired, select the options to store this information as new road segments are added to the road theme. If you have a large road theme dataset, this can cause the performance of PEGGER to be affected. This feature can be turned on and off as desired. Snapping Start Editing the Road Theme ArcView allows you to edit a theme that is based on an ArcView shapefile if you have file write permission on the shapefile. To make a shapefile theme editable To undo and redo edits To save your edits and continue editing To save your edits out to a new theme To stop editing a theme and commit your edits Select the pegging tool To start pegging a new road first select the pegging
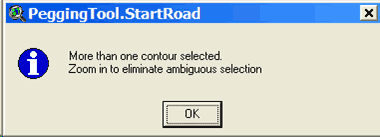
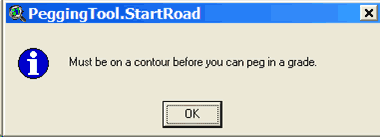
tool The Pegging tool will only be available when there is an editable line theme in the view, otherwise it will be grayed out and unavailable for use. Start a new road To start a new road with the Pegging tool, hold down the shift key while clicking on a contour line in the view. Pegging will begin when you click on a single contour line. If PEGGER cannot determine which contour is the desired start point then the following information will be displayed:
If PEGGER cannot find any contours then the following information will be displayed:
If you are having problems then zoom in Add a section of road A section of road will be pegged in when you click
in the general direction you want the road to go. The current grade
can be set
using either the right-click popup menu, the road grade selection
under the Road menu or the Pegger Toolbar.
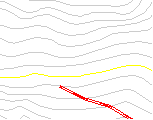
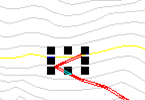
Peg a road Unintentional Switchback
If we click anywhere towards the left the road continues on in the same direction.
If we click to the right instead, we create a switchback on some rather steep ground. This particular switchback is not feasible due to steep grade and ground slope.
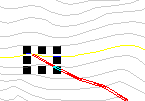
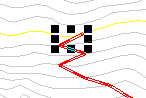
If care is not taken to choose the proper direction for the road to go a situation like to following may occur. Here the user clicked directly up the hill from the end of the road so switchback after switchback was created. This is not a feasible design!
If a section of road is added and you wish to delete it you can use the Undo command under the Edit menu or pres Ctrl+Z. You will have to start over again at the end of the road by setting the snap environment so it snaps to the end of the road then shift clicking. Valleys Ridges Snap road to existing roads For more help on ArcView’s snapping capabilities look up “snapping” in
the help index or use the help tool To stop editing a theme and commit your edits Dissolve After locating a route with Pegger there will be many segments of adjoining road that may have the same attributes. It may be desirable to join these adjacent segments into single parts to reduce data storage requirements or for additional analysis. The Dissolve function will merge adjacent features based on a common attribute. Dissolve can be used on an entire theme, or just the selected features of a theme. The output of the dissolve function is a new shapefile. The Dissolve Lines function works only on polyline themes. Dissolve Lines will not work in an edit session.
Merge As the pegging tool places roads it creates many short line segments of road. There are a few reasons you may want to merge these short line segments into one large one. If you want to use the spline tool to smooth a pegged road then you must merge the segments first. If you want to survey multiple segments of a pegged road, it must first be merged into a single feature. Also, you may want to merge short segments to decrease the size of your feature attribute table. To merge segments you must be editing the theme. Undo is available.
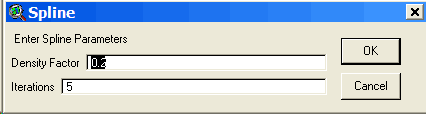
If the merge process creates undesirable results use Undo to go back. Spline As a final edit to your new road (or to an existing road) you may want to smooth it by using a spline function. The spline function smoothes jagged road segments by rounding pegged segment intersections. Caution must be used when splining as vertices are moved during the process. The spline function does not create true curves or follow traditional road layout techniques. It is a strictly mathematical spline function and its applicability to road engineering is questionable. It is included as a Pegger function as some have asked for it. To spline a road segment you must be editing the theme. Undo is available.
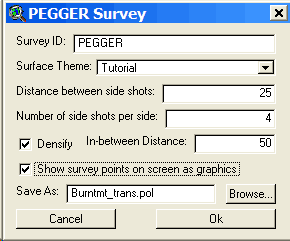
If the spline process creates undesirable results use Undo to go back. Attribute Grades If you have a road theme that has been previously pegged, the attribute grades function can be used to assign road grades to the segments. If your road theme or contour theme is large and attributing grades to the features as the road is being pegged slows the software, then attributing the grades after completing the pegging work can be more efficient. Please note that if any changes have been made to the road theme or the contour theme after pegging the segments, or if the grade can not be determined, then the attribute grades function will assign values of 9999 to the segments. Generally, it is more efficient to attribute road grades to the feature as they are being pegged. This can be done by running Setup Pegger under the Roads menu with the road theme selected. Survey Pegger can export a digital road survey to RoadEng® for detailed road design. Pegger exports digital road surveys in the Criterion Unit Survey .pol format. If there are other formats that you would like to use, please contact Luke Rogers at lwrogers@u.washington.edu and send an example file with documentation. To survey a pegged road for export to RoadEng, either ArcView Spatial or 3D Analyst must be installed and enabled. To enable Spatial or 3D Analyst select Extensions under the File menu. In addition, a valid GRID data source or TIN data source must be in the active view and a single polyline feature selected. Pegger will only survey single polyline features. If you have a road made of many polyline segments, merge or dissolve the features into a single feature. To use the survey function select Survey P-Line from the Roads menu. This will bring up a dialog where you can specify an 8 character survey name (PEGGER by default), the surface theme to use (either a GRID or TIN) and some survey options.
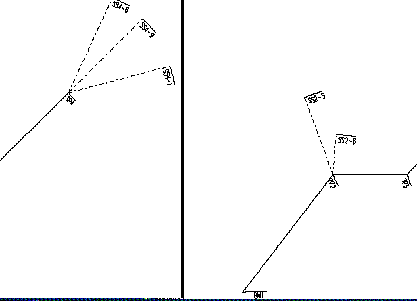
The Distance between side shots is the horizontal distance between side-shot elevation values, perpendicular to the road or on an angle bisector if the side shots are at a Turning Point (TP). The Number of side-shots per side is the number of elevation values to collect on each side of the P-Line. If your data is stored in feet and the Distance between side-shots is 25 and the number of side-shots per side is 4, then 4 side shots will be taken at 25 foot intervals up to 100 feet away from the road on each side of the P-Line. By default, Pegger only surveys the elevation surface at turning points. If you would like to survey the elevation surface at a regular interval that is denser than the turning points then select Densify and enter a distance between survey points. Optionally, the survey points can be drawn in the active view as graphics. This allows you to see the points where Pegger is surveying the elevation surface and preview what will be imported into RoadEng. By default, Pegger will name the output unit survey .pol file with the same name as the shapefile being surveyed and place it in the same directory. If you would like to specify an alternate location or name, select Browse… Importing Survey into RoadEng Unit Survey data can be imported into the Terrain Module using menu File - Insert File. The Import Unit Survey Options Dialog allows you to control the format of the incoming data. The unit survey format reads raw survey shot data. It is very useful for downloading general survey information such as radial surveys or digital data collected with a Laser Gun. The file contains foreshots, backshots and side shots. The coordinates of each leg of the traverse are calculated based on the azimuth, inclination and distance. When a traverse contains loops, adjustments for closure are not automatic. Foreshots, backshots and multiple shots for the same leg of a traverse are averaged. The file is in ASCII format with fields delimited by commas. Each record contains the following fields:
For Measurement types FS, BS and SD the following fields are included in the record:
For Measurement types SR the following fields are included in the record:
Unit Survey Importing Procedure In RoadEng Terrain Module:
Example TRAV1,SR,1420,2230,1311,BM1 TRAV1,BS,2,1,180:30:00,.356,120,0,0 TRAV1,FS,1,2,75:30:00,.356,120,0,0,TP2 TRAV1,SD,2,5,340:30:00,.12,67,0,0,SS2-5 TRAV1,SD,2,6,5:30:00,.12,33,0,0,SS2-6 TRAV1,FS,2,3,90:30:00,.256,60,0,0,TP3 TRAV1,FS,3,4,45:30:00,.12,93,0,0,TP4 TRAV1,SD,4,8,25:30:00,.12,85,0,0,SS4-8 TRAV1,SD,4,9,45:30:00,.12,85,0,0,SS4-9 TRAV1,SD,4,10,75:30:00,.12,85,0,0,SS4-10
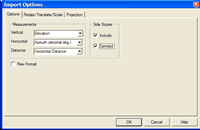
Import Unit Survey Options Dialog Source: Softree RoadEng 4 Terrain Module Help file This dialog box is accessed through the Options button of the Import Setup Dialog, when item Unit Survey is selected. See also Importing Unit Survey Data.
Additional Features While all of the uses of Pegger can not be envisioned there are a few things that others have found useful in its use. Additional datasets can be used to guide in the initial placement of pegged roads. Streams, side-slope information, unstable areas, protected lands, and other GIS datasets can be very useful. Questions, Enhancements & Bugs Any comments or questions about Pegger can be sent to: Luke Rogers |